Group Kappelle
Group Kappelle
About 8 out 10 strokes are ischemic, and once blood flow to the brain is interrupted, brain cells start to die. More than 70% of stroke survivors have lifelong neurological symptoms such as weakness or paralysis in their arms or legs or difficulty speaking.
Current treatments for acute ischemic stroke are thrombectomy (intra-arterial removal of a blood clot) and intravenous thrombolysis (injection of a drug that breaks up the clot). Both must be administered within several hours of the stroke to be beneficial. Part of our research focuses on how to improve these treatments.
The main results of the MR CLEAN trial
In deze folder bevindt zich extra informatie door middel van een video. Scan de bovenste QR-code met uw telefoon om deze video te bekijken. Of bekijk de video via:
Time is brain uitklapper, klik om te openen
The most important thing for a patient with an acute ischemic stroke is early treatment to prevent as little brain injury as possible. This sudden event is usually caused by a clot in a blood vessel in the brain. In 2015, we participated ina Dutch multicenter clinical trial and showed for the first time that thrombectomy treatment (intra-arterial removal of the blood clot) is effective within 6 hours of a stroke onset. This has revolutionized care for stroke patients.
We’ll soon embark on a new clinical trial to determine if, under certain circumstances, patients may benefit from a thrombectomy after 6 hours.
MR CLEAN results in a new standard of care uitklapper, klik om te openen
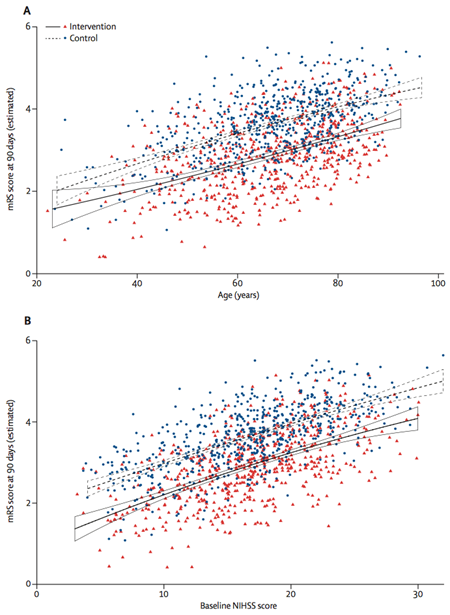
The MR CLEAN clinical trial in the Netherlands showed for the first time, that most patients benefit from receiving a thrombectomy within 6 hours after a stroke, with a 10-15% chance of better functional outcome. Since then, intra-arterial trombectomy has become the new standard in medical care for acute ischemic stroke patients.
Extending the window of time uitklapper, klik om te openen
The time between the occurrence of a stroke and administration of treatment varies widely, due to assessment time, blood tests, referrals, imaging and diagnosis. Needless to say, the 6-hour timeframe for beneficial outcome of a thrombectomy is short. Thus, in order to determine which patients would benefit from a thrombectomy outside of the 6-hour window, we need to identify which factors presented by a patient’s case can expect a favorable outcome.
Will thrombectomy become the better treatment for acute ischemic stroke? uitklapper, klik om te openen
While a thrombectomy requires a skilled intervention radiologist, another treatment, intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) administers a therapeutic drug via an IV in the arm. The drug, tissue-type plasminogen activator, dissolves the clot in the brain and is of proven value when given within 3 to 4.5 hours of a stroke. Nowadays, a substantial number of patients who can be treated with thrombectomy also receive IVT. This is of concern however, since IVT can induce bleeding in the brain or in other parts of the body and studies are unclear about whether giving IVT before a thrombectomy is beneficial. We’re therefore investigating whether patients can receive a thrombectomy without IVT.
Our aim is to be able to treat more patients with thrombectomy by optimizing treatment and extending the window of time within which we can treat patients.






