Infection and Immunity nieuws
Infection and Immunity nieuws
Bacterial metabolites involved in risk of IBD and colorectal cancer
PhD research by Coco Duizer (UMC Utrecht) provides insights into the detrimental effects of bacterial-derived metabolites (in particular ADP-heptose and butyrate) on the intestinal epithelium. This was accomplished using Fusobacterium nucleatum and Campylobacter jejuni, which also provided insights into pathogenic effects of these bacterial species. The results expand existing knowledge on microbiota-derived metabolites in intestinal diseases such as IBD, colorectal cancer and acute gastroenteritis.
Read moreHeart attack risk temporarily increased after severe influenza in adults without known cardiovascular disease

An infection with the influenza virus ("flu") temporarily increases the risk of a heart attack, especially in individuals without a history of hospitalization for heart problems. This is according to a Dutch study led by University Medical Center (UMC) Utrecht among more than 23,000 adults who had a severe influenza infection between 2008 and 2019.
Read moreJun 20: IgA antibody therapy may be a viable alternative therapy in high-risk neuroblastoma
PhD research by Marjolein Stip has shown that IgA-based antibody therapy may be a viable alternative for IgG anti-GD2 antibody therapy in the treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma. In vitro studies suggest that IgA-based therapy (in contrast to IgG-based antibodies) is not associated with neuropathic pain while maintaining clinical efficacy.
Read moreJun 7: A critical appraisal of clinical decision support systems for immune diseases

This PhD thesis by Marianne Messelink (UMC Utrecht) describes the development, validation and evaluation of clinical decision support systems for rheumatoid arthritis and primary antibody deficiency. Such systems have the potential to advance diagnoses and optimize treatments. However, there are also challenges and pitfalls in their development and implementation. Ultimately, the focus should not be on the predictive value, but on the real benefit to the patient and healthcare system.
Read moreJun 6: Lymphocyte dynamics in a more natural mouse model
Lymphocyte dynamics research by Elena de Dios Panal (UMC Utrecht) shows that animal models provided valuable information that could hardly or not at all be obtained from humans. However, the discrepancies between human and murine immune dynamics found in parts of this thesis highlight some fundamental differences between murine and human immune cell maintenance. While animal models still hold potential, their critical discussion remains crucial.
Read morePatricia Bruijning-Verhagen appointed professor of vaccination and infection control epidemiology

Utrecht University and UMC Utrecht have announced the appointment of Patricia Bruijning-Verhagen as professor of vaccination and infection control epidemiology, effective June 1, 2024. This position will enable Patricia to continue her work in designing and evaluating optimal infection prevention policies through vaccination and other innovative strategies. Her appointment comes at a crucial time, as the world faces the dual challenge of emerging infectious diseases and an expanding portfolio of vaccines.
Read moreJune 3: Life span of lymphocytes further unraveled

In her PhD thesis, Carina Bruckmaier (UMC Utrecht) explored lymphocyte dynamics in various tissue sites in homeostasis and during imbalanced states. In particular, her research on the life span of some of the lymphocyte subcategories revealed some interesting new insights.
Read moreMay 29: Unveiling the mysteries of smell: research on COVID-19-related smell loss
During the COVID-19 pandemic – especially during the first wave of infections- a large number of people infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus reported a sudden loss of smell. Dutch investigators quickly set up a series of studies on diagnosis, pathophysiology, epidemiology, clinical course and treatment of COVID-19-induced loss of smell. The PhD thesis by Emma Schepens (UMC Utrecht) provides some interesting and valuable insights on this unexpected clinical finding.
Read moreMay 27: New research provides further evidence that pediatric uveitis is a systemic immune disease
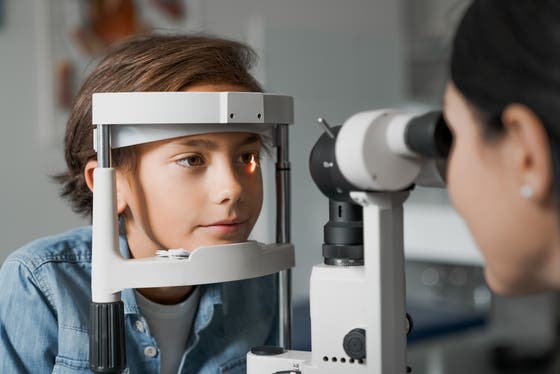
Pediatric uveitis might be a manifestation of a disease that affects not only the eye but also the systemic immune system and microcirculation. Therefore, it is important to adopt a multidisciplinary approach in the management of pediatric uveitis patients to provide the best possible care. These were the main takeaways from the PhD research by Carlyn Kouwenberg from UMC Utrecht.
Read moreAlternatives to antibiotics: Adapting phages to overcome bacterial defense barriers
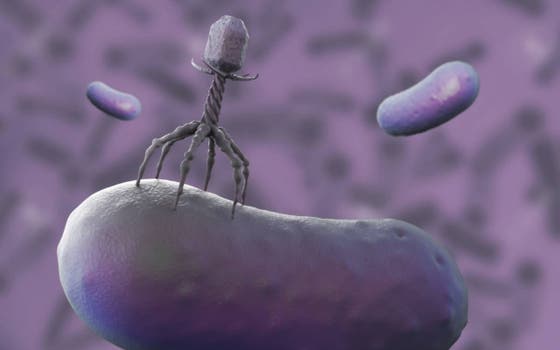
Collaborating researchers from University Medical Center Utrecht and Delft University of Technology have received funding from the Dutch Research Council (NWO) to develop more broadly acting bacteriophages. With help of such adapted phages, the researchers want to overcome bacterial defense barriers, which are important mechanisms in the bacterial resistance against bacteriophages.
Read more
